An overactive bladder is a frustrating medical condition that can hinder your life.
While lifestyle changes and pelvic floor muscle training can make a difference, results may take a while to kick in or you may see no change at all. Treatment with Botox injections, however, has been proven to be highly effective in controlling urinary incontinence.
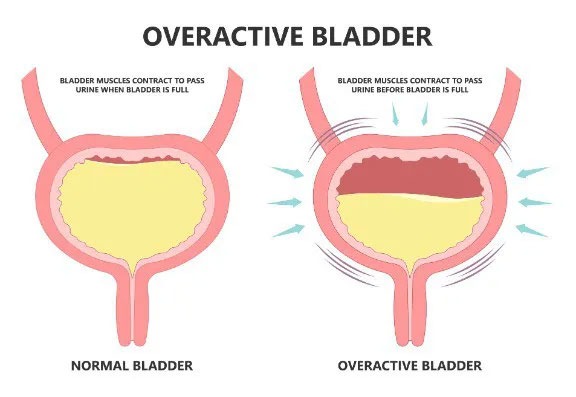
An overactive bladder is when the muscles of the bladder start to contract on their own, even when the volume of urine in your bladder is low. These are called involuntary contractions, and they create an urgent need to urinate.
An overactive bladder can affect people of all ages and is often associated with urge incontinence, which happens when someone feels an overwhelming need to urinate immediately.
Bladder overactivity can also cause other issues such as frequent urination, painful urination, urinary tract infections, urinary incontinence and urinary leakage.
In some cases, people with an overactive bladder may also have trouble emptying their bladders completely because they tend to experience urgent urinary incontinence. This means that they may not be able to get rid of all the urine in their bladder before they feel a strong urge to go again.
An overactive bladder can be caused by a number of factors, including neurological disorders, diabetes and hormonal changes.
How Can Botox Help Overactive Bladders?
Botox is a brand name for botulinum toxin – a neurotoxin which blocks the messages sent by nerves to the bladder muscles.
When botulinum toxin is used to treat an overactive bladder these signals are blocked and the muscles relax, which reduces the frequency of the muscles contracting which causes an overactive bladder.
Botulinum toxin also relieves symptoms such as an urgent need to urinate and leaking urine.
How Does Using Botox for an Overactive Bladder Work?
An anaesthetic gel will be placed into the urethra to numb the area of the Botox injections. A thin tube called a cystoscope is then inserted into the bladder, before your practitioner injections the botulinum toxin through this tube into specific areas of the wall of the bladder muscle.
Botox injections take approximately five minutes and you may feel a pricking sensation or slight discomfort.
Before you go home, your practitioner may ask you to pass urine and want to scan your bladder to ensure it is emptying appropriately.
You may also be prescribed antibiotics to go home with. Normal activities can usually resume the day after Botox injections.
You should start noticing a difference in your bladder activity after two weeks. Botox injection results to treat an overactive bladder treatment generally last three to six months.
How Much Does It Cost to Treat an Overactive Bladder With Botox?
Botox for overactive bladder treatment is sometimes available for free on the NHS.
Speak to your GP to see if you qualify.
Private botulinum toxin treatment is generally around £500 but will depend on the location and experience of the practitioner.
Are There Side Effects to Treating Overactive Bladders With Botox?
Botox side effects are rare, but can include:
-
Urinary retention: difficulty or inability to empty your bladder – can be treated with a catheter
-
Blood in urine: usually minor and settles down
-
Urinary tract infection: treatable with antibiotics
In extreme circumstances, you may experience difficulty breathing, swallowing or speaking.
If you experience any Botox side effects or complications, contact your practitioner immediately.
As using botulinum toxin to treat an overactive bladder is a medical treatment, it's really important you see a medically-qualified practitioner with specific training in this area.
They should have undergone training in anatomy and physiology, as well as being accountable to a regulatory body such as the General Medical Council (GMC), Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC), or General Dental Council (GDC).
They should also be able to advise you of the risks of injectable botulinum toxin treatment and be confident in handling complications if they arise.

Author: Anna Kremerov
Mrs Anna Kremerov is an award-winning Nurse Practitioner known for Aesthetic Medicine and non-surgical procedures. She is the Founder of Anna Medical Aesthetics, the only CQC registered aesthetic medical practice in Swindon and a MaiLi Centre of Excellence for the South West of England.
Anna and her team have built up an impeccable reputation with over a hundred 5-star patient reviews on Google and Trustpilot.
Anna has over 22 years of combined medical experience in Intensive Care, Woman Health, Primary Care and Aesthetics Medicine.
To view more blogs by Anna Kremerov please click here.
