Botox, a term that often conjures images of ageless skin and celebrity endorsements, has a history as fascinating as the results it produces. Its journey from a scientific discovery to a cosmetic staple is a testament to the marvels of medical science. But beyond its surface appeal, Botox is a complex biological product with a myriad of uses, both cosmetic and therapeutic.
Let's delve into the heart of Botox, exploring its essence and how it works. This is not just a tale of vanity but a story of scientific innovation and the quest for well-being.
Quick Summary
- Botox is a brand name for botulinum toxin type A
- Used to reduce wrinkles by relaxing muscles
- It also treats medical conditions like migraines
- Temporary effects, lasting 3-6 months
- Safety and preparation are crucial
For more detailed information please see below.

What is Botox?
Botox, known scientifically as Botulinum toxin type A, is not just a beauty enhancer. This toxin, derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, plays a dual role in the medical and cosmetic world. It's like the Swiss Army knife of the medical toolkit: versatile and effective.
Botox is a neuromodulator at its core, meaning it alters nerve impulses, leading to muscle relaxation. This ability makes it an invaluable tool in softening the appearance of wrinkles, which are often the result of repetitive muscle contractions. However, Botox's prowess extends beyond cosmetic applications, serving therapeutic roles in treating conditions such as muscle spasms and migraines.
The Science Behind Botox
At the heart of Botox's transformative powers is a fascinating interplay of biology and chemistry. It targets the nervous system, specifically the junctions where nerve cells meet muscles. Botox temporarily blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for triggering muscle contractions. This blockade prevents the muscles from contracting, leading to a relaxation that smooths out wrinkles and softens facial expressions.
But the influence of Botox extends beyond cosmetic enhancement; it's a therapeutic agent, offering relief in various medical conditions like chronic migraines, where it prevents the nerve signals that cause pain. In essence, Botox acts as a masterful conductor, silencing the unwanted symphony of overactive muscles and nerves, creating a harmonious balance within the body's complex systems.
Cosmetic Applications of Botox
In the world of aesthetics, Botox is like an artist's brush, delicately altering the canvas of the human face. Its primary use in cosmetic enhancement is to reduce the appearance of wrinkles, particularly those that appear from repetitive facial expressions, such as frown lines, crow's feet, and forehead lines. Botox smooths the skin by relaxing the underlying muscles, offering a rejuvenated appearance.
Beyond mere wrinkle reduction, Botox's precision allows for subtle lifting effects, like an eyebrow lift, which can open up the face and impart a more youthful and rested look. This non-invasive procedure has gained immense popularity for its ability to enhance natural beauty without surgery.

Medical Uses of Botox
Botox's utility extends into the medical field, serving as a key player in managing various health conditions. It's particularly effective in treating chronic migraines, offering relief to those who suffer from this debilitating condition. By preventing the neurotransmitter release that triggers pain pathways, Botox can reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
Additionally, Botox can treat hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), providing a life-changing solution for individuals dealing with this condition. It works by blocking the nerves that activate sweat glands, significantly reducing sweat production.
Botox's medical applications showcase its versatility and effectiveness, making it a valuable tool in neurology and dermatology. Its ability to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with diverse conditions is a testament to the neurotoxin's broad potential.
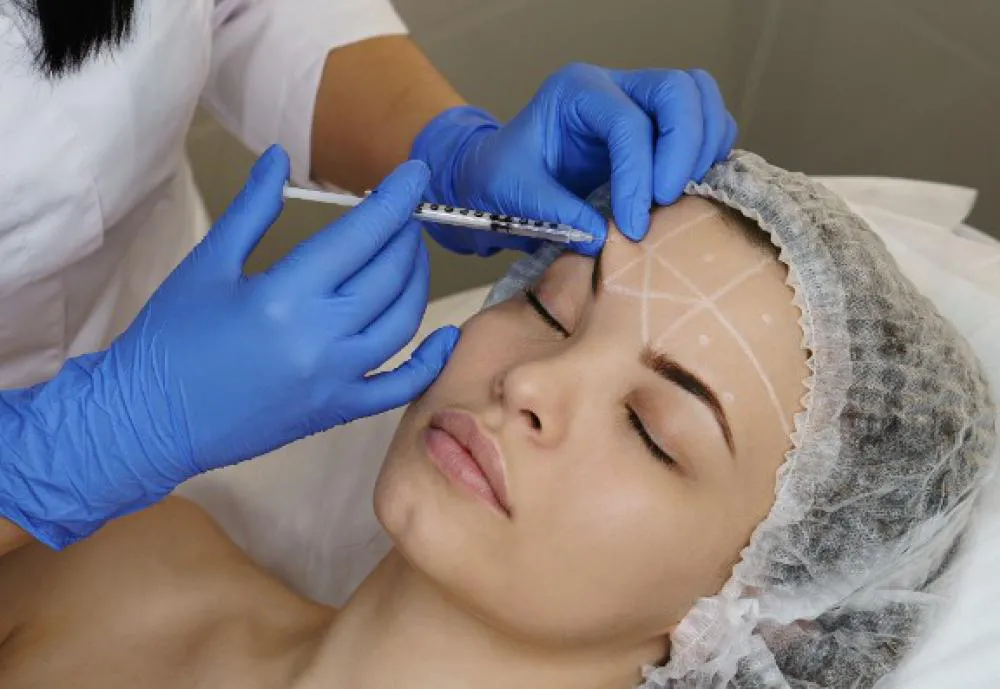
The Procedure of Administering Botox
The journey of receiving Botox is a blend of art and science. It starts with a consultation with your chosen medical practitioner to discuss goals and evaluate suitability. The target areas are cleaned during the procedure, and small amounts of Botox are injected using a fine needle. This process is typically quick and minimally uncomfortable, allowing patients to return to their daily activities immediately.
The practitioner's skill is crucial; they must understand facial anatomy to ensure natural-looking results and avoid complications. Post-treatment, patients are advised to avoid rubbing the treated areas and to limit strenuous activities for a short period to ensure the Botox remains localized.
Safety and Side Effects of Botox
Botox, while widely considered safe, comes with its share of potential side effects.
Commonly, patients might experience temporary bruising, swelling, or redness at the injection sites. More rare but serious effects can include muscle weakness, difficulties in swallowing, or breathing issues, particularly if the toxin spreads beyond the treatment area. Individuals must seek treatment from qualified medical professionals and discuss their medical history to mitigate risks.
Effectiveness and Duration of Botox
The effects of Botox are not immediate; it typically takes a few days to see the initial changes, with the full impact visible in about two weeks. The cosmetic improvements last around 3 to 6 months, after which the muscles gradually regain their function, and the treated areas return to their previous appearance.
Regular follow-up treatments can help maintain the desired effects longer. Botox's longevity varies depending on the individual's metabolism, the area treated, and the amount of product used.
Comparing Botox with Other Treatments
Botox stands out in the cosmetic world for its specific ability to relax muscles and smooth wrinkles, unlike dermal fillers, which add volume to the skin.
While Botox is excellent for expression lines, fillers are better for deep wrinkles or volume loss. Additionally, treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy target skin texture and tone, not muscle activity.
Conclusion
With Botox, the future of non-invasive treatments looks promising, offering a blend of efficacy, safety, and accessibility.
Book Your Botox Consultation Today
As you will have learnt, Botox is a great tool to help you look younger and fresher. It’s important that you get treated by an experienced, medically trained, and qualified practitioner who will inject you safely.
As always, if you have any questions you can use our Botox Q&A where you can ask for more advice direct from a trusted, experienced medical practitioner.

Author: Anna Kremerov
Mrs Anna Kremerov is an award-winning Nurse Practitioner known for Aesthetic Medicine and non-surgical procedures. She is the Founder of Anna Medical Aesthetics, the only CQC registered aesthetic medical practice in Swindon and a MaiLi Centre of Excellence for the South West of England.
Anna and her team have built up an impeccable reputation with over a hundred 5-star patient reviews on Google and Trustpilot.
Anna has over 22 years of combined medical experience in Intensive Care, Woman Health, Primary Care and Aesthetics Medicine.
